Jump table
The jump table is a method to transfer program control to another code block using a table of branch or jump instructions.
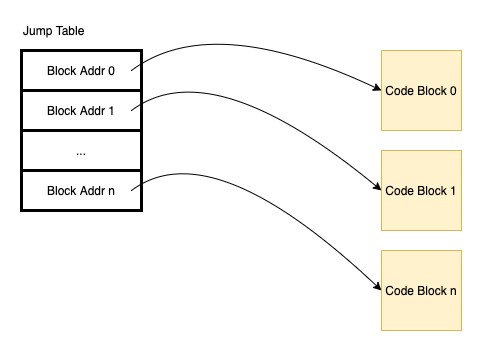
It’s a table of code addresses, that can be indexed by selector value. We can use a selector to map to a code address and jump to the code block.
Approximate translation:
target = JumpTable[selector];
goto target;
The jump table can be used by the compiler to optimize switch-case in many programming languages. Each switch case is defined as its memory address in the table jump.
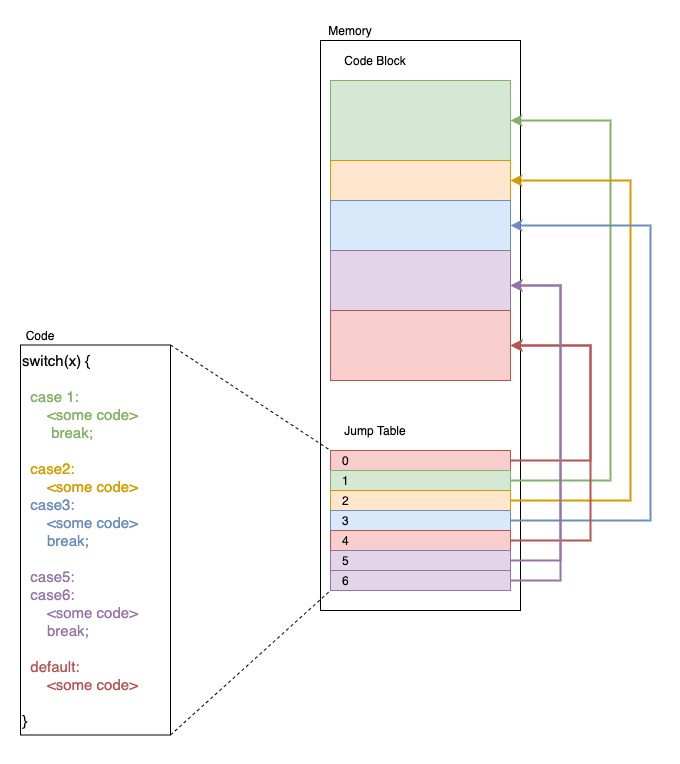
The selector can be calculated by data (input of switch-case) and transformed into an offset that is used at the selector in the jump table. The transform can be multiplying or shifting.
selector = start-address-of-jump-table + offset
offset = option-index * memory-size-one-address
option-index = transform(data)
If a static translate table is used, this multiplying can be performed manually or by the compiler, without any run time cost.
References: